Public Static Website
Overview
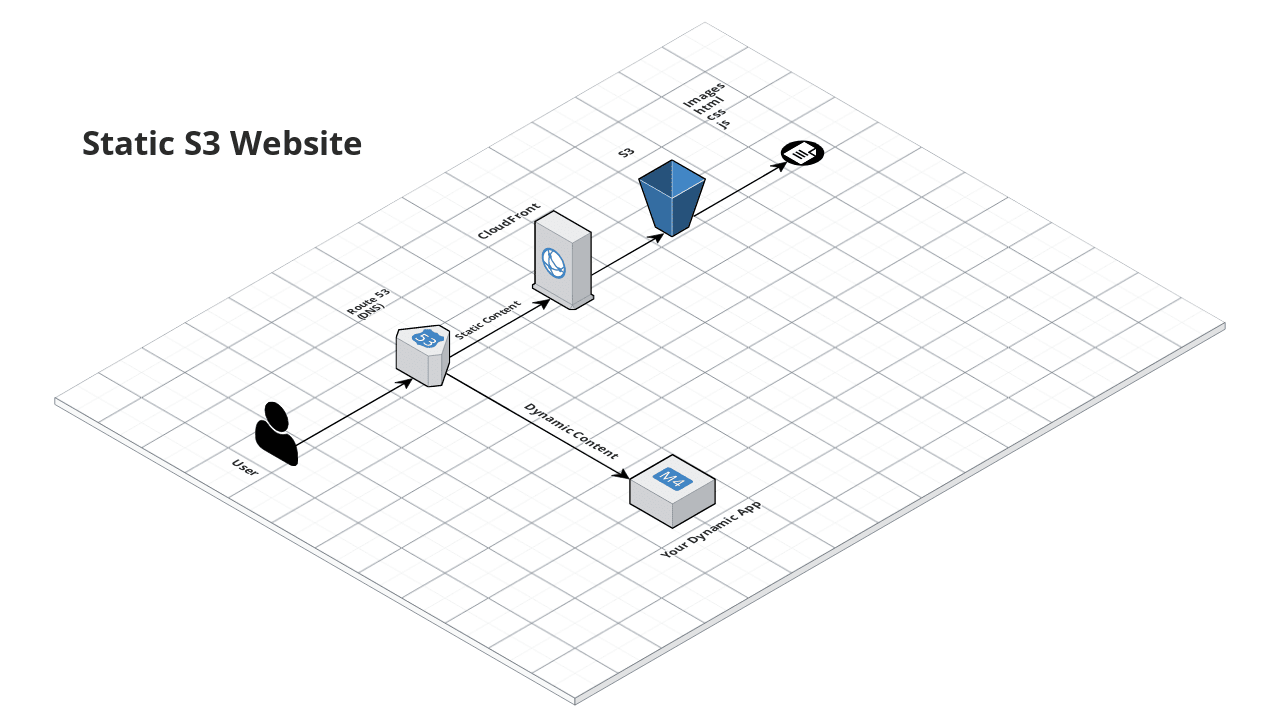
This service creates a public static website using S3 and CloudFront on AWS. The website can contain static HTML, CSS, JS, and images.
 Static S3 Website
Static S3 Website
Features
Offload storage and serving of static content (HTML, CSS, JS, images) to a public S3 bucket configured as a website.
Create additional buckets to store your website access logs, and your CloudFront access logs.
Deploy a CloudFront Distribution in front of the public S3 bucket for your website domain.
Optionally:
- Create a Route 53 entry in IPV4 and IPV6 formats to route requests to your domain name to the public S3 bucket,
- And associate an existing TLS certificate issued by Amazon’s Certificate Manager (ACM) for your domain.
Learn
Serving static content from S3 rather than from your own app server can significantly reduce the load on your server, allowing it to focus on serving dynamic data. This saves money and makes your website run faster. For even bigger improvements in performance, deploy a CloudFront Content Distribution Network (CDN) in front of the S3 bucket.
note
This repo is a part of the Gruntwork Service Catalog, a collection of reusable, battle-tested, production ready infrastructure code. If you’ve never used the Service Catalog before, make sure to read How to use the Gruntwork Service Catalog!
Core concepts
This module deploys a public website, so the S3 bucket and objects with it are readable by the public. It also is
hosted in a Public Hosted Zone in Route 53. You may provide a hosted_zone_id in variables,
or you may provide the base_domain_name associated with your Public Hosted Zone in Route 53, optionally along with
any tags that must match that zone in base_domain_name_tags. If you do the latter, this module will find the hosted
zone id for you.
For more info on why you would use S3 to store static content, why you may want a CDN in front of it, how to access the website, and how to configure SSL, check out the documentation for the s3-static-website and s3-cloudfront modules.
- Quick Start
- How to test the website
- How to configure HTTPS (SSL) or a CDN?
- How to handle www + root domains
- How do I configure Cross Origin Resource Sharing (CORS)?
Repo organization
- modules: the main implementation code for this repo, broken down into multiple standalone, orthogonal submodules.
- examples: This folder contains working examples of how to use the submodules.
- test: Automated tests for the modules and examples.
Deploy
Non-production deployment (quick start for learning)
If you just want to try this repo out for experimenting and learning, check out the following resources:
- examples/for-learning-and-testing folder: The
examples/for-learning-and-testingfolder contains standalone sample code optimized for learning, experimenting, and testing (but not direct production usage).
Production deployment
If you want to deploy this repo in production, check out the following resources:
- examples/for-production folder:
The
examples/for-productionfolder contains sample code optimized for direct usage in production. This is code from the Gruntwork Reference Architecture, and it shows you how we build an end-to-end, integrated tech stack on top of the Gruntwork Service Catalog.
Reference
- Inputs
- Outputs
acm_certificate_domain_name— The domain name for which an ACM cert has been issued (e.g. *.foo.com). Only used ifcreate_route53_entryis true. Set to blank otherwise.
base_domain_name— The domain name associated with a hosted zone in Route 53. Usually the base domain name ofwebsite_domain_name(e.g. foo.com). This is used to find the hosted zone that will be used for the CloudFront distribution. Ifcreate_route53_entryis true, one ofbase_domain_nameorhosted_zone_idmust be provided.
base_domain_name_tags— The tags associated withbase_domain_name. If there are multiple hosted zones for the samebase_domain_name, this will help filter the hosted zones so that the correct hosted zone is found.
create_route53_entry— If set to true, create a DNS A Record in Route 53. Ifcreate_route53_entryis true, one ofbase_domain_nameorhosted_zone_idmust be provided.
custom_tags— A map of custom tags to apply to the S3 bucket containing the website and the CloudFront distribution created for it. The key is the tag name and the value is the tag value.
default_ttl— The default amount of time, in seconds, that an object is in a CloudFront cache before CloudFront forwards another request in the absence of an 'Cache-Control max-age' or 'Expires' header.
error_document— The path to the error document in the S3 bucket (e.g. error.html).
force_destroy— If set to true, this will force the delete of the website, redirect, and access log S3 buckets when you run terraform destroy, even if there is still content in those buckets. This is only meant for testing and should not be used in production.
geo_locations_list— The ISO 3166-1-alpha-2 codes for which you want CloudFront either to distribute your content (ifgeo_restriction_typeis whitelist) or not distribute your content (ifgeo_restriction_typeis blacklist).
geo_restriction_type— The method that you want to use to restrict distribution of your content by country: none, whitelist, or blacklist.
hosted_zone_id— The ID of the Route 53 Hosted Zone in which to create the DNS A Records specified inwebsite_domain_name. Ifcreate_route53_entryis true, one ofbase_domain_nameorhosted_zone_idmust be provided.
index_document— The path to the index document in the S3 bucket (e.g. index.html).
max_ttl— The maximum amount of time, in seconds, that an object is in a CloudFront cache before CloudFront forwards another request to your origin to determine whether the object has been updated. Only effective in the presence of 'Cache-Control max-age', 'Cache-Control s-maxage', and 'Expires' headers.
min_ttl— The minimum amount of time that you want objects to stay in CloudFront caches before CloudFront queries your origin to see whether the object has been updated.
routing_rules— A json array containing routing rules describing redirect behavior and when redirects are applied. For routing rule syntax, see: https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AWSCloudFormation/latest/UserGuide/aws-properties-s3-websiteconfiguration-routingrules.html. This will only be used ifshould_redirect_all_requestsis false
viewer_protocol_policy— Use this element to specify the protocol that users can use to access the files in the origin specified by TargetOriginId when a request matches the path pattern in PathPattern. One of allow-all, https-only, or redirect-to-https.
website_domain_name— The name of the website and the S3 bucket to create (e.g. static.foo.com).
cloudfront_access_logs_bucket_arn— The ARN of the created S3 bucket associated with the website's CloudFront access logs.
cloudfront_domain_names— The domain names created for the CloudFront Distribution. Should be the same as the inputwebsite_domain_name.
cloudfront_id— The CloudFront ID of the created CloudFront Distribution.
website_access_logs_bucket_arn— The ARN of the created S3 bucket associated with the website access logs.
website_s3_bucket_arn— The ARN of the created S3 bucket associated with the website.